What is artificial intelligence (AI)? (CSS-2016)
Back in the 1950s, the fathers of the field Minsky and McCarthy, described artificial intelligence as any task performed by a program or a machine that, if a human carried out the same activity, we would say the human had to apply intelligence to accomplish the task.
According to the father of Artificial Intelligence, John McCarthy, it is “The science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs”.
Artificial Intelligence is a way of making a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or a software think intelligently, in the similar manner the intelligent humans think.
AI is accomplished by studying how human brain thinks, and how humans learn, decide, and work while trying to solve a problem, and then using the outcomes of this study as a basis of developing intelligent software and systems.
Philosophy of Artificial Intelligence
While exploiting the power of the computer systems, the curiosity of human, lead him to wonder, “Can a machine think and behave like humans do?”
Thus, the development of AI started with the intention of creating similar intelligence in machines that we find and regard high in humans.
Read also: 20 Greatest Discoveries of Modern Science and Their Implications
What are the uses for Artificial Intelligence?
AI is ubiquitous today, used to recommend what you should buy next online, to understand what you say to virtual assistants such as Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri, to recognise who and what is in a photo, to spot spam, or detect credit card fraud.
Programming Without and With Artificial Intelligence
The programming without and with AI is different in following ways
| Programming Without Artificial Intelligence | Programming With Artificial Intelligence |
| A computer program without AI can answer the specific questions it is meant to solve. | A computer program with AI can answer the generic questions it is meant to solve. |
| Modification in the program leads to change in its structure.
|
AI programs can absorb new modifications by putting highly independent pieces of information together. Hence you can modify even a minute piece of information of program without affecting its structure. |
| Modification is not quick and easy. It may lead to affecting the program adversely. | Quick and Easy program modification. |
What are the different types of Artificial Intelligence?
At a very high level artificial intelligence can be split into two broad types: narrow AI and general AI.
Narrow AI is what we see all around us in computers today: intelligent systems that have been taught or learned how to carry out specific tasks without being explicitly programmed how to do so.
This type of machine intelligence is evident in the speech and language recognition of the Siri virtual assistant on the Apple iPhone, in the vision-recognition systems on self-driving cars, in the recommendation engines that suggest products you might like based on what you bought in the past. Unlike humans, these systems can only learn or be taught how to do specific tasks, which is why they are called narrow AI.
What can narrow AI do?
There are a vast number of emerging applications for narrow AI: interpreting video feeds from drones carrying out visual inspections of infrastructure such as oil pipelines, organizing personal and business calendars, responding to simple customer-service queries, co-ordinating with other intelligent systems to carry out tasks like booking a hotel at a suitable time and location, helping radiologists to spot potential tumors in X-rays, flagging inappropriate content online, detecting wear and tear in elevators from data gathered by IoT devices, the list goes on and on.
What can general AI do?
Artificial general intelligence is very different, and is the type of adaptable intellect found in humans, a flexible form of intelligence capable of learning how to carry out vastly different tasks, anything from haircutting to building spreadsheets, or to reason about a wide variety of topics based on its accumulated experience. This is the sort of AI more commonly seen in movies, the likes of HAL in 2001 or Skynet in The Terminator, but which doesn’t exist today and AI experts are fiercely divided over how soon it will become a reality.
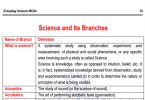
Read also: Science and its Branches
A survey conducted among four groups of experts in 2012/13 by AI researchers Vincent C Müller and philosopher Nick Bostrom reported a 50 percent chance that Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) would be developed between 2040 and 2050, rising to 90 percent by 2075. The group went even further, predicting that so-called ‘ superintelligence’ — which Bostrom defines as “any intellect that greatly exceeds the cognitive performance of humans in virtually all domains of interest” — was expected some 30 years after the achievement of AGI.
That said, some AI experts believe such projections are wildly optimistic given our limited understanding of the human brain, and believe that AGI is still centuries away.
What is machine learning?
There is a broad body of research in AI, much of which feeds into and complements each other.
Currently enjoying something of a resurgence, machine learning is where a computer system is fed large amounts of data, which it then uses to learn how to carry out a specific task, such as understanding speech or captioning a photograph.
What are neural networks?
Key to the process of machine learning are neural networks. These are brain-inspired networks of interconnected layers of algorithms, called neurons, that feed data into each other, and which can be trained to carry out specific tasks by modifying the importance attributed to input data as it passes between the layers. During training of these neural networks, the weights attached to different inputs will continue to be varied until the output from the neural network is very close to what is desired, at which point the network will have ‘learned’ how to carry out a particular task.
A subset of machine learning is deep learning, where neural networks are expanded into sprawling networks with a huge number of layers that are trained using massive amounts of data. It is these deep neural networks that have fueled the current leap forward in the ability of computers to carry out task like speech recognition and computer vision.
There are various types of neural networks, with different strengths and weaknesses. Recurrent neural networks are a type of neural net particularly well suited to language processing and speech recognition, while convolutional neural networks are more commonly used in image recognition. The design of neural networks is also evolving, with researchers recently refining a more effective form of deep neural network called long short-term memory or LSTM, allowing it to operate fast enough to be used in on-demand systems like Google Translate.
Applications of AI
AI has been dominant in various fields such as −
- Gaming − AI plays crucial role in strategic games such as chess, poker, tic-tac-toe, etc., where machine can think of large number of possible positions based on heuristic knowledge.
- Natural Language Processing − It is possible to interact with the computer that understands natural language spoken by humans.
- Expert Systems − There are some applications which integrate machine, software, and special information to impart reasoning and advising. They provide explanation and advice to the users.
- Vision Systems − These systems understand, interpret, and comprehend visual input on the computer. For example,
- A spying aeroplane takes photographs, which are used to figure out spatial information or map of the areas.
- Doctors use clinical expert system to diagnose the patient.
- Police use computer software that can recognize the face of criminal with the stored portrait made by forensic artist.
- Speech Recognition − Some intelligent systems are capable of hearing and comprehending the language in terms of sentences and their meanings while a human talks to it. It can handle different accents, slang words, noise in the background, change in human’s noise due to cold, etc.
- Handwriting Recognition − The handwriting recognition software reads the text written on paper by a pen or on screen by a stylus. It can recognize the shapes of the letters and convert it into editable text.
- Intelligent Robots − Robots are able to perform the tasks given by a human. They have sensors to detect physical data from the real world such as light, heat, temperature, movement, sound, bump, and pressure. They have efficient processors, multiple sensors and huge memory, to exhibit intelligence. In addition, they are capable of learning from their mistakes and they can adapt to the new environment.
Check Other NOTES for General Science & Ability
- Science Myths Exposed: Unraveling the Truth Behind Them
- Science and its Branches
- Black Hole: What’s expected inside it? (CSS Paper 2007, 2018 Solution)
- Discuss the Function of Kidneys in Human Body (CSS Paper 2015 Solution)
- How solar eclipse and lunar eclipse are caused? (CSS Paper 2015 Solution)
- Different Branches of Science | General Science Notes
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) | CSS General Science & Ability Notes
- ‘Artificial Intelligence’ for humanity | General Science & Ability Notes
- What are Landslide and What Causes | General Science & Ability Notes
- Weather and Climate | General Science and Ability Notes







[…] Read also: Artificial Intelligence (AI) | CSS General Science & Ability Notes […]