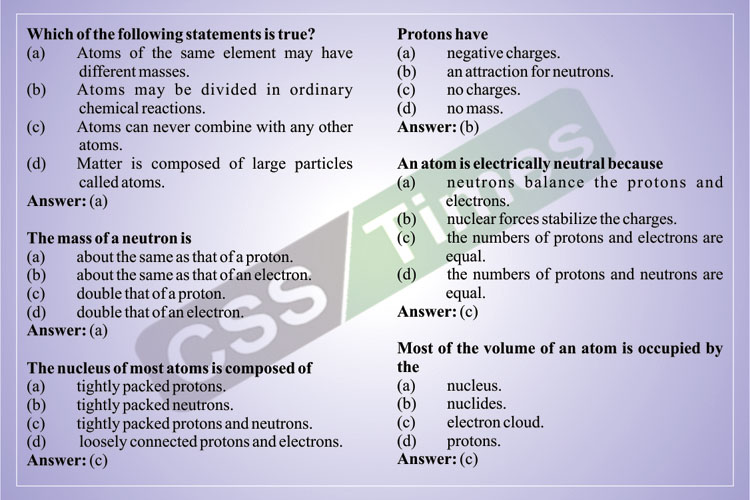
Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Atoms of the same element may have different masses.
(b) Atoms may be divided in ordinary chemical reactions.
(c) Atoms can never combine with any other atoms.
(d) Matter is composed of large particles called atoms.
Answer: (a)
The mass of a neutron is
(a) about the same as that of a proton.
(b) about the same as that of an electron.
(c) double that of a proton.
(d) double that of an electron.
Answer: (a)
The nucleus of most atoms is composed of
(a) tightly packed protons.
(b) tightly packed neutrons.
(c) tightly packed protons and neutrons.
(d) loosely connected protons and electrons.
Answer: (c)
Check Also: Industrial and Agricultural Revolution | Notes for CSS / PMS
Protons have
(a) negative charges.
(b) an attraction for neutrons.
(c) no charges.
(d) no mass.
Answer: (b)
An atom is electrically neutral because
(a) neutrons balance the protons and electrons.
(b) nuclear forces stabilize the charges.
(c) the numbers of protons and electrons are equal.
(d) the numbers of protons and neutrons are equal.
Answer: (c)
Most of the volume of an atom is occupied by the
(a) nucleus.
(b) nuclides.
(c) electron cloud.
(d) protons.
Answer: (c)
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different
(a) principal chemical properties.
(b) masses.
(c) numbers of protons.
(d) numbers of electrons.
Answer: (b)
Atoms of the same element that have different masses are called
(a) moles.
(b) isotopes.
(c) nuclides.
(d) neutrons.
Answer: (b)
Isotopes of an element contain different numbers of
(a) electrons.
(b) protons.
(c) neutrons.
(d) nuclides.
Answer: (c)
All isotopes of hydrogen contain
(a) one neutron.
(b) two electrons.
(c) one proton.
(d) two nuclei.
Answer: (c)
Helium-4 and helium-3 are
(a) isotopes.
(b) different elements.
(c) compounds.
(d) nuclei.
Answer: (a)
Check Also: General Science and Ability MCQs Solved (Exercise-1)
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is its
(a) atomic number.
(b) Avogadro constant.
(c) mass number.
(d) number of neutrons.
Answer: (c)
As the mass number of the isotopes of an element increases, the number of protons
(a) decreases.
(b) increases.
(c) remains the same.
(d) doubles each time the mass number increases
Answer: (c)
All atoms of the same element have the same
(a) atomic mass.
(b) number of neutrons.
(c) mass number.
(d) atomic number
Answer: (d)
Atoms of the same element can differ in
(a) chemical properties.
(b) mass number.
(c) atomic number.
(d) number of protons and electrons.
Answer: (b)
The average atomic mass of an element is the average of the atomic masses of its
(a) naturally occurring isotopes.
(b) two most abundant isotopes.
(c) nonradioactive isotopes.
(d) artificial isotopes.
Answer: (a)
The average atomic mass of an element
(a) is the mass of the most abundant isotope.
(b) may not equal the mass of any of its isotopes.
(c) cannot be calculated.
(d) always adds up to 100.
Answer: (b)
The atomic mass listed in the periodic table is the
(a) average atomic mass.
(b) relative atomic mass of the most abundant isotope.
(c) relative atomic mass of the most stable radioactive isotope.
(d) mass number of the most abundant isotope.
Answer: (a)
An aluminum isotope consists of 13 protons, 13 electrons, and 14 neutrons. Its mass number is
(a) 13.
(b) 14.
(c) 27.
(d) 40.
Answer: (c)
Diamond is a very expensive ornament. It is composed of a single element: (CSS-2009)
(a) Carbon
(b) Gold
(c) Silver
(d) Platinum
(e) None of these
Answer: (a)
Carbon-14 (atomic number 6), the radioactive nuclide used in dating fossils, has
(a) 6 neutrons.
(b) 8 neutrons.
(c) 10 neutrons.
(d) 14 neutrons.
Answer: (b)
Silicon-30 contains 14 protons. It also contains
(a) 16 electrons
(b) 16 neutrons.
(c) 30 neutrons
(d) 44 neutrons
Answer: (b)
The part of the atom where the electrons CANNOT be found is the
(a) area surrounding the nucleus.
(b) nucleus.
(c) electron cloud.
(d) orbital’s.
Answer: (b)
How many quantum numbers are needed to describe the energy state of an electron in an atom?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer: (d)
The spin quantum number of an electron can be thought of as describing
(a) the direction of electron spin.
(b) whether the electron’s charge is positive or negative.
(c) the electron’s exact location in orbit.
(d) the number of revolutions the electron makes about the nucleus per second.
Answer: (a)
Check Also: Important and Most Wanted MCQs about Current Federal Cabinet of Pakistan
How many electrons are needed to completely fill the fourth energy level?
(a) 8
(b) 18
(c) 32
(d) 40
Answer: (c)
How is an electron’s principal quantum number symbolized?
(a) s (b) p
(c) n (d) d
Answer: (c)
A chemical bond between atoms results from the attraction between the valence electrons and—–of different atoms.
(a) Nuclei
(b) Inner electrons
(c) Isotopes
(d) Lewis structures
Answer: (a)
A covalent bond consists of
(a) A shared electron.
(b) A shared electron pair.
(c) Two different ions.
(d) An octet of electrons.
Answer: (b)
If two covalently bonded atoms are identical, the bond is identified as
(a) nonpolar covalent.
(b) Polar covalent.
(c) Ionic.
(d) Dipolar.
Answer: (a)
A covalent bond in which there is an unequal attraction for the shared electrons is
(a) nonpolar.
(b) Polar.
(c) Ionic.
(d) Dipolar.
Answer: (b)
Atoms with a strong attraction for electrons they share with another atom exhibit
(a) Zero electronegativity.
(b) Low electronegativity.
(c) High electronegativity.
(d) Lewis electronegativity.
Answer: (c)
Bonds that possess between 5% and 50% ionic character are considered to be
(a) Ionic.
(b) Pure covalent.
(c) Polar covalent.
(d) nonpolar covalent.
Answer: (c)
The greater the electro negativity difference greater the bond’s percentage of
(a) Ionic character.
(b) nonpolar character. between two atoms bonded together, the
(c) Metallic character.
(d) Electron sharing.
Answer: (a)
The notation for sodium chloride, NaCl , stands for one
(a) formula unit.
(b) molecule.
(c) crystal.
(d) atom.
Answer: (a)
In a crystal of an ionic compound, each cation is surrounded by a number of
(a) Molecules.
(b) Positive ions.
(c) Dipoles.
(d) Negative ions.
Answer: (d)
Compared with the neutral atoms involved in the formation of an ionic compound, the crystal lattice that results is
(a) Higher in potential energy.
(b) Lower in potential energy.
(c) Equal in potential energy.
(d) Unstable.
Answer: (b)
The lattice energy of compound A is greater in magnitude than that of compound B. What can be concluded from this fact?
(a) Compound A is not an ionic compound.
(b) It will be more difficult to break the bonds in compound A than those in compound B.
(c) Compound B has larger crystals than compound A.
(d) Compound A has larger crystals than compound B.
Answer: (b)
The forces of attraction between molecules in a molecular compound are generally
(a) Stronger than the attractive forces among formula units in ionic bonding.
(b) Weaker than the attractive forces among formula units in ionic bonding.
(c) Approximately equal to the attractive forces among formula units in ionic bonding.
(d) Equal to zero.
Answer: (b)
If the electronic structure of oxygen atom is written as 1s2 2s2 2p4 it would violate
(a) Hund’s rule
(b) Paulis exclusion principle
(c) Both Hund’s and Pauli’s principles
(d) None of these
Answer: (d)
Number of nodal planes for f-orbital are
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer: (a)
Three isotopes of an element have mass numbers M, (M + 1) and (M + 2). If the mean mass number is (M + 0.5) than which of the following ratio may be accepted for M , (M + 1) , (M + 2) in that order.
(a) 1 : 1 : 1
(b) 4 : 1 : 1
(c) 3 : 2 : 1
(d) 2 : 1 : 1
Answer: (b)
Check Also: Energy Resources MCQs (Set-I) | General Science and Ability
A possible set of quantum numbers for the last electron added to a gallium atom (Z = 31) in its ground state is n l m ms
(a) 4 1 –1 +1/2
(b) 4 0 0 –1/2
(c) 3 2 +2 +1/2
(d) 3 0 0 –1/2
Answer: (a)
An atom has four unpaired electrons. The total spin of this atom will be
(a) 1
(b) 1.5
(c) 2
(d) 4
Answer: (c)
A type of chemical bond that is formed from the attraction of an atom that has lost an electron for an atom that has gained an electron is called a(n)
(a) Covalent bond.
(b) Ionic bond.
(c) Metallic bond
(d) Hydrogen bond
Answer: (b)







[…] Atomic Structure MCQs | General Science and Ability Solved MCQs […]
[…] Atomic Structure MCQs | General Science and Ability Solved MCQs […]