Q: Describe different methods to estimate the age of the Universe (CSS-2018)
Methods for Measuring the Age of the Universe
When we speak of “the age of the Universe,” we’re talking about how much time has past since the Universe could first be described by the hot Big Bang until the present day.
According to research, the universe is approximately 13.8 billion years old. How did scientists determine how many candles to put on the universe’s birthday cake? They can determine the age of the universe using two different methods:
1. Age of galaxies from the travel time of light
2. Age of the universe from expansion
Under the laws of General Relativity, if you have a Universe like ours, which is:
- of uniform density on the largest scales,
- which has the same laws and general properties at all locations,
- which is the same in all directions, and
- in which the Big Bang occurred at all locations everywhere at once, then there is a unique connection between how old the Universe is and how it’s expanded throughout its history.
In other words, if we can measure how the Universe is expanding today and how it has expanded throughout its entire history, we can know exactly what all the different components are that make it up. We learn this from a whole host of observations, including:
- From direct measurements of the brightnesses and distances of objects in the Universe such as stars, galaxies and supernovae, allowing us to construct the cosmic distance ladder
- From measurements of large-scale-structure, the clustering of galaxies, and from baryon acoustic oscillations
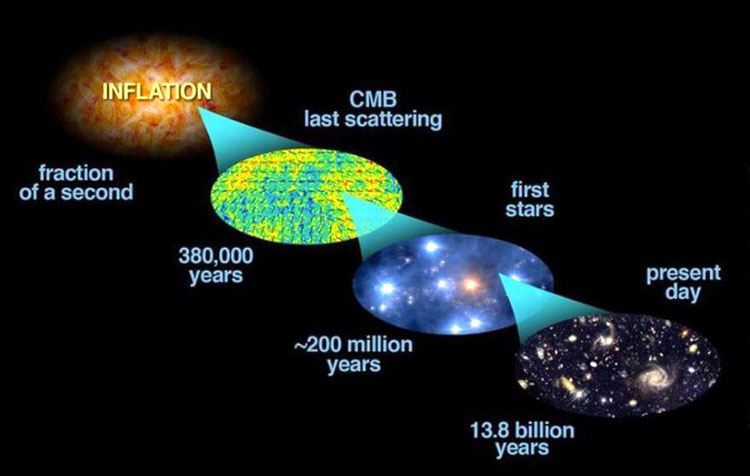
- And from the fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background, a “snapshot” of the Universe when it was a mere 380,000 years old.
You put all of these things together, and you get a Universe that is made up, today, of 68% dark energy, 27% dark matter, 4.9% normal matter, about 0.1% neutrinos, about 0.01% radiation, and pretty much nothing else. But you throw in how the Universe is expanding today, and we can extrapolate this back in time, and learn the entire expansion history of the Universe, and hence, its age.
The number we get — most precisely from Planck but augmented from the other sources like supernova measurements, the HST key project and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey — is that the Universe is 13.81 billion years old, with an uncertainty of just 120 million years. This means we’re confident in the age of the Universe to 99.1% accuracy, which is an amazing feat!
If the Universe had the same current properties today but were made of 100% normal matter and no dark matter or dark energy, our Universe would be only 10 billion years old. If the Universe were 5% normal matter (with no dark matter or dark energy) and the Hubble constant were 50 km/s/Mpc instead of 70 km/s/Mpc, our Universe would be a whopping 16 billion years old. With the combinations of things we have today, however, we can confidently state 13.81 billion years is the age of the Universe, with a very small uncertainty. It’s an incredible feat of science.
Definition for Universe
The universe is defined as everything that exists, has existed, and will exist including all physical space, time, matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space The universe is currently estimated at roughly 13.7 billion years old, give or take 130 million years. In comparison, the solar system is only about 4.6 billion years old. This estimate came from measuring the composition of matter and energy density in the universe.
- Astronomy is the science which investigates all the matter-energy in the universe: its distribution, composition, physical states, movements, and evolution. It is concerned with the evolution, physics, chemistry, meteorology, and motion of celestial objects, as well as the formation and development of the Universe. Astronomy is one of the oldest sciences
- Cosmology: Astronomy also includes cosmology, which is the study of the structure, origin, and evolution of the universe. Cosmology is the branch of astronomy involving the origin and evolution of the universe, from the Big Bang to today and on into the future. According to NASA, the definition of cosmology is “the scientific study of the large scale properties of the universe as a whole.”
- Astrology is not to be confused with Astronomy, which is a natural scientific study of celestial objects, such as stars, planets, comets, nebulae, star clusters and galaxies. Astrology is the study of the movements and relative positions of celestial bodies interpreted as having an influence on human affairs and the natural world. In other words, this consists of a number of belief systems which hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world. If astrology is defined as a study does it make a science? No, many fields like philosophy or theology are defined as a study and are not sciences.
Evolution of Cosmolgical Theories
Cosmology is the study of universe as a whole, including its distant past and its future. It is the study of the general nature of the universe. What is the universe now? What was it in the past and what is it likely to be in the future? How was the universe created? These are the basic themes of cosmology. Men have been examining and wondering about the sky for many millennia. As scientific discoveries have been made, ideas about the origin of the universe have changed and are still changing
Ptolemy’s Geocentric Theory
A Geocentric theory is an astronomical theory which describes the universe as a geocentric system, i.e., a system which puts the Earth in the center of the universe, and describes other objects from the point of view of the Earth. Ptolemy proposed his geocentric theory in the 2nd century A.D. According to his theory, the earth stood at the center, surrounded by some eight spheres, the Moon, the Sun, the stars, and the five other planets known till the time: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn.
The geocentric theory was considered to be profoundly mistaken at that time. Since the advent of relativity theory in the early 1900s, the laws of physics have been written in covariant equations, meaning that they are equally valid in any frame. Heliocentric and geocentric plotting systems are both used today, depending on which allows more convenient calculations.
Sun centered Universe (Heliocentric Theory)
In the early 1500s, when virtually everyone believed Earth was the center of the universe, Polish scientist Nicolaus Copernicus proposed that the planets instead revolved around the sun. Although his model wasn’t completely correct, it formed a strong foundation for future scientists to build on and improve mankind’s understanding of the motion of heavenly bodies.
Copernicus’ ideas, published only two months before he died, took nearly a hundred years to seriously take hold. When Galileo Galilei claimed in 1632 that Earth orbited the sun, building upon the Polish astronomer’s work, he found himself under house arrest for committing heresy against the Catholic Church
Despite this, the observations of the universe proved the two men correct in their understanding of the motion of celestial bodies. Today, we call the model of the solar system, in which the planets orbit the sun, a heliocentric or Copernican model.
Origion of the Universe
In 1959 a survey was conducted of scientists across America concerning their understanding of the physical sciences. One particular question asked “What is your concept of the age of the Universe?” More than two thirds of the scientists polled responded that there was no origin of the Universe. They believed that the Universe was eternal.
Then five years later, in 1964, radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson discovered a microwave signal buried in their data. They attempted to filter out the signal, assuming that it was merely unwanted noise. However, they soon realized what the signal actually was; they had inadvertently discovered the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). The CMB had been predicted by a theory that few believed at the time called the Big Bang. This discovery was the first evidence that the Universe had a beginning